Advanced Features
Unified Unsubscription
Taking the vue framework as an example, if the stream is imported into a vue component from elsewhere and you want the subscription to be automatically canceled after the component is destroyed, you can use the thenPlugin of plugin for unified handling:
import { getCurrentScope, onScopeDispose } from "vue";
import { Stream } from "fluth";
const promise$ = new Stream();
promise$.plugin.then.push((unsubscribe) => {
if (getCurrentScope()) onScopeDispose(unsubscribe);
});Nodes subscribed in the vue single-file setup function will automatically unsubscribe when the vue component is destroyed, avoiding memory leaks.
Unified Error Handling
Use the executePlugin of plugin to handle errors of nodes uniformly:
import { Stream } from "fluth";
const promise$ = new Stream();
promise$.plugin.execute.push((promise) =>
promise.catch((err) => {
console.error(err);
})
);Stream Branching
Stream branching refers to triggering the execution of another stream's nodes within one stream.
Triggering Stream Flow
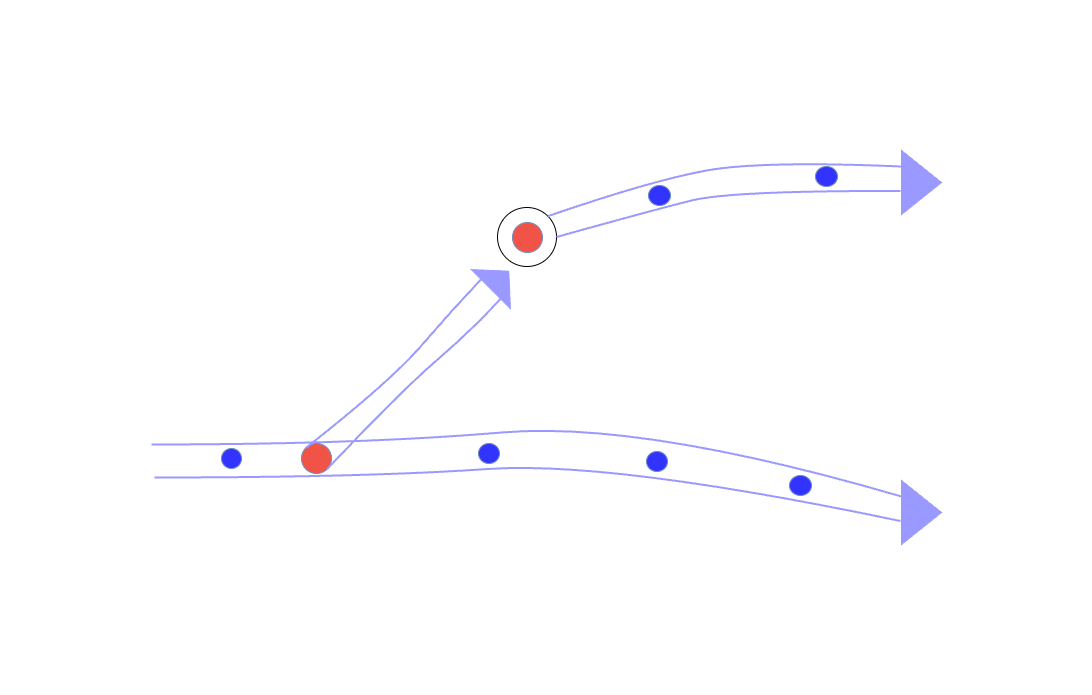
Triggering Stream nodes allows pushing data:
import { Stream } from "fluth";
const promise1$ = new Stream();
const subjection1$ = promise1$.then((data) => console.log(data));
const promise2$ = new Stream();
// Trigger another stream within one stream
const subjection2$ = promise2$.then((data) => {
promise1$.next(data + 1);
});Triggering Subjection Flow
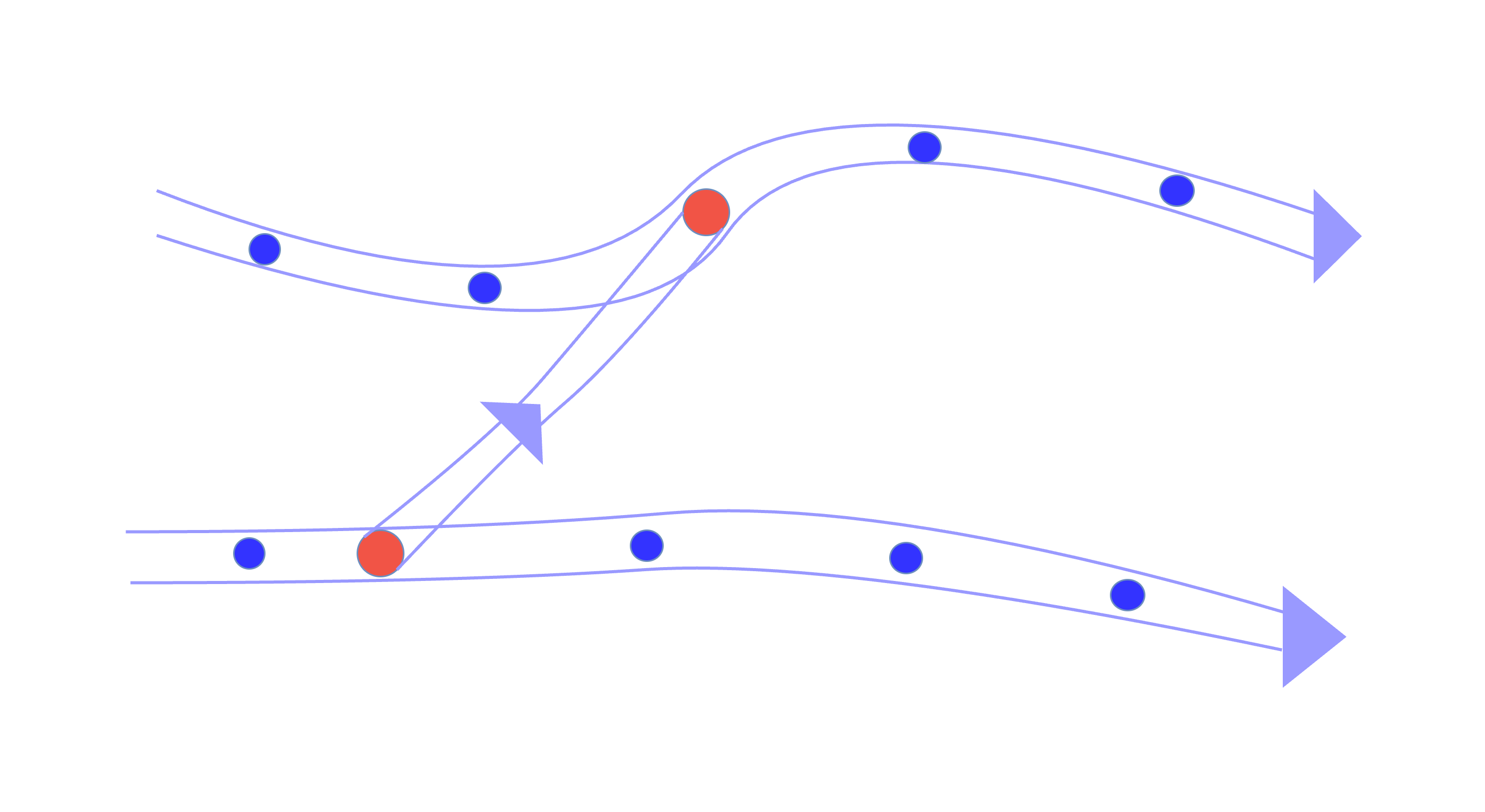 Triggering Subjection node cannot push data:
Triggering Subjection node cannot push data:
import { Stream } from "fluth";
const promise1$ = new Stream();
const subjection1$ = promise1$.then((data) => console.log(data));
const promise2$ = new Stream();
// Trigger another stream within one stream
const subjection2$ = promise2$.then((data) => {
subjection1$.execute();
});Stream Merging
If you need to merge data from multiple streams, you should look at operators like combine, merge, concat, etc., to perform stream merging.